A shock absorber is a component used in industrial equipment. Simply put, it works by using internal oil and specialized structures to convert the kinetic energy generated during machine operation into heat energy, thereby reducing impact, vibration, and noise in various industrial machines.
The following image shows the internal structure of a shock absorber.
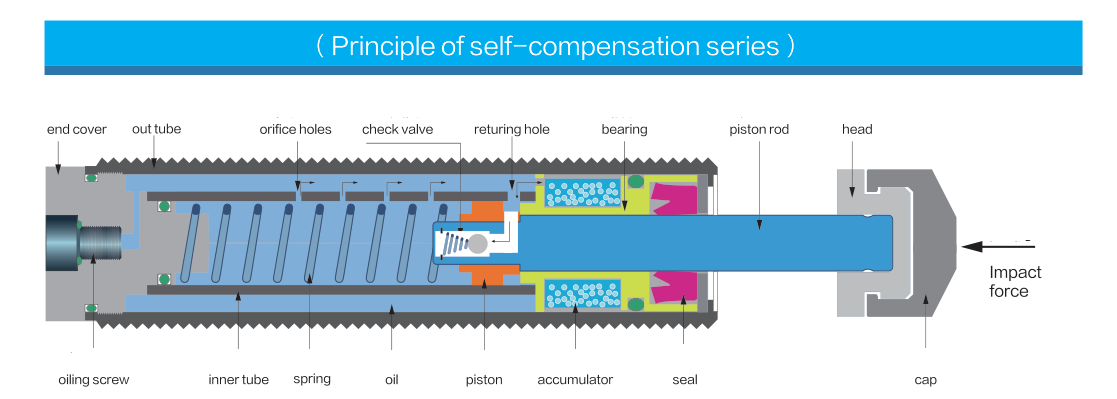
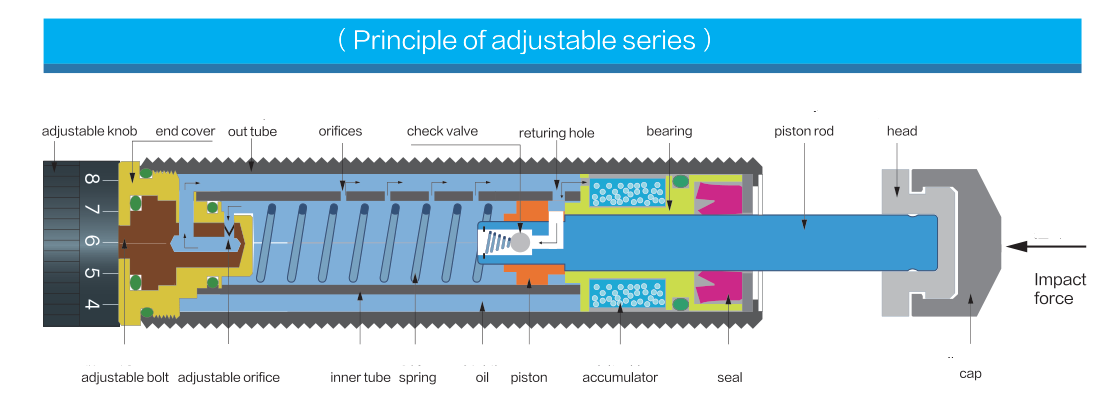
Why Use a Shock Absorber?
The main reasons for using a shock absorber are:
1.Protecting and maintaining equipment, and extending its service life.
2.Reducing noise during the operation of large machinery.
3.Ensuring precise operation by preventing product displacement on assembly lines.
4.Protecting worker safety.

Typical Applications of Shock Absorbers
Shock absorbers are widely used in various types of industrial equipment. Common applications include:
1.Various industrial automation equipment
2.Large amusement equipment
3.Military industry
4.Photovoltaic and wind power industries
5.Medical equipment industry
6.Medium and high-voltage power transmission and distribution industry
Comparison Between Shock Absorbers and Other Cushioning Devices
Unlike other cushioning products made of rubber, springs, or pneumatic devices, shock absorbers are specifically designed for industrial equipment and deliver significantly better performance.
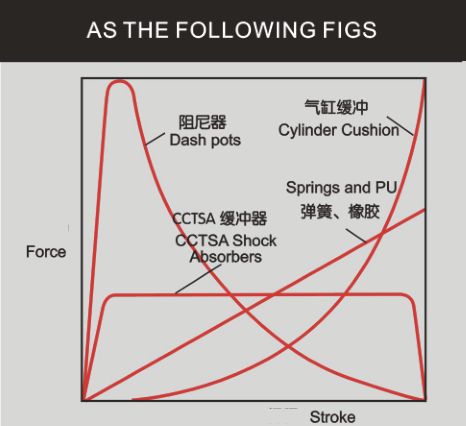
1. Rubber-Based Cushioning
Principle: Rubber is compressed and stores energy like a spring, then quickly rebounds.
Problem: It can temporarily absorb impact, but the energy isn’t truly dissipated. Instead, it's “stored” in the rubber and released again, much like a bouncing ball, making it prone to rebound.
Advantage: Inexpensive and easy to install.
Disadvantage: Low absorption efficiency, high rebound, not suitable for high-precision or high-impact industrial environments.
2. Spring-Based Cushioning
Principle: Similar to rubber—it compresses and stores energy, then rebounds.
Problem: It converts impact energy into elastic force without dissipating it, which causes rebound.
Advantage: Simple structure.
Disadvantage: Noticeable rebound and poor impact absorption.
3. Pneumatic Cushioning
Principle: Absorbs impact by compressing air, which is released through small holes.
Problem: If the release is too fast or too slow, it loses balance and causes rebound similar to a spring.
Advantage: Better than rubber and springs; can partially release energy.
Disadvantage: If not well-controlled, it still causes rebound, and the absorption effect is unstable.
4. Hydraulic Cushioning (shock absorber)
Principle: Uses the resistance of oil flow—especially the "velocity-squared resistance" that increases with speed—to truly absorb and dissipate impact energy by converting it into heat.
Result: No rebound, and extremely high absorption efficiency.
Advantage: Can absorb large impacts even with a compact size; precise control; stable absorption performance; very effective in protecting equipment.
ToYou Shock Shock Absorber Products
Post time: Jul-23-2025






